Plastic containers are essential components across multiple industries, playing a pivotal role in packaging, storage, and consumer goods. These versatile products serve a wide range of functions, from food and beverage packaging to household storage solutions and industrial transport containers. Offering an excellent alternative to traditional materials like glass and metal, plastic containers provide a lightweight, durable, and cost-effective solution to meet the diverse needs of modern consumers.
With increasing demand for sustainable and innovative packaging solutions, understanding the design principles and manufacturing techniques behind plastic container molds is becoming more critical. In this analysis, we will explore the key stages of mold development, from the initial conceptual design to the precision fabrication that shapes the final product. By examining these processes, we’ll uncover how the design of plastic container molds affects both product performance and production efficiency.

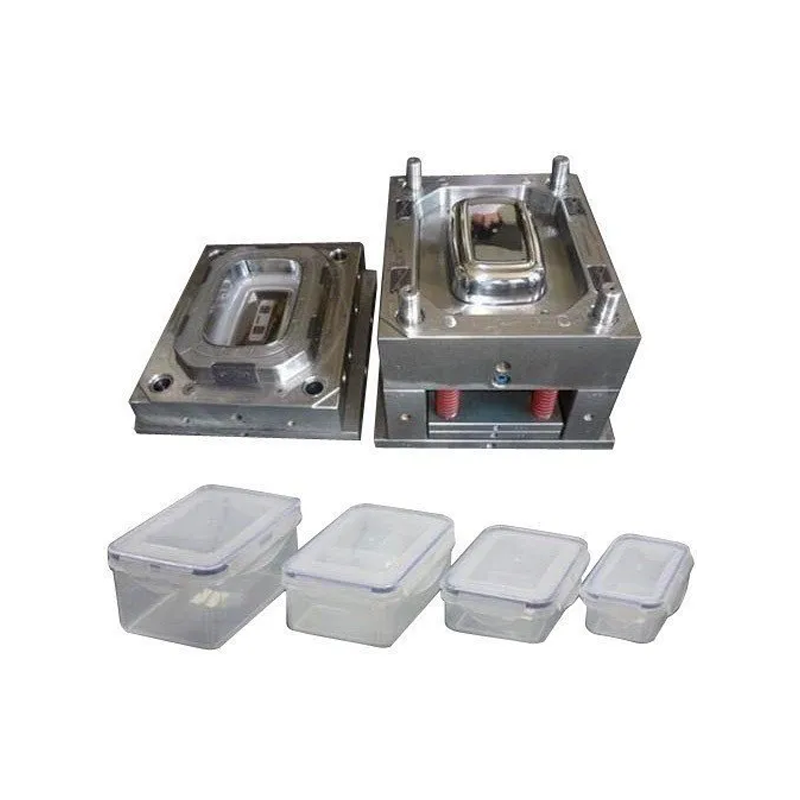
What Is a Plastic Container Mold?
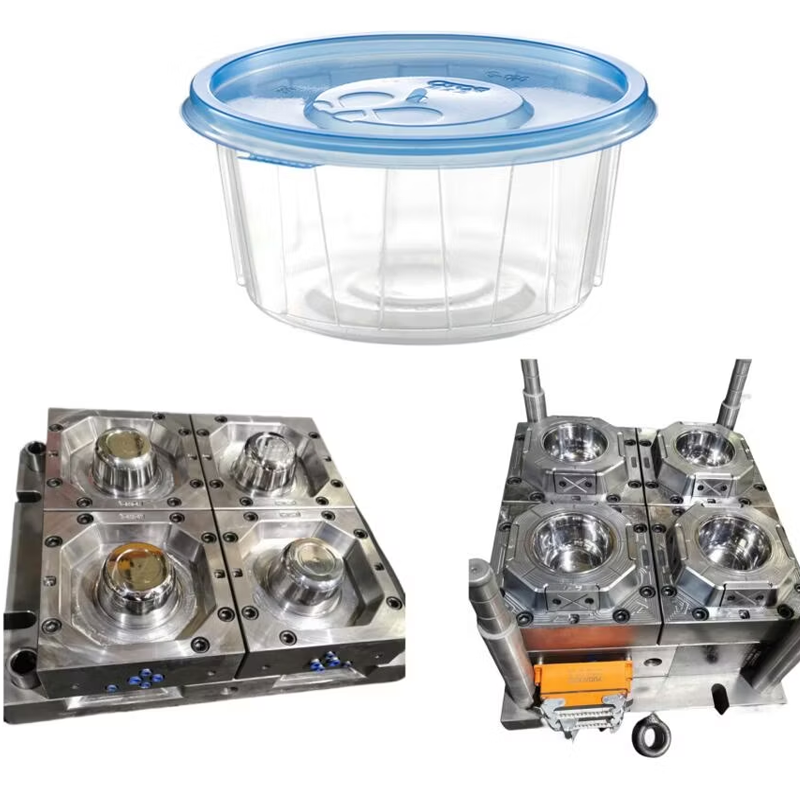
A plastic container mold is a specialized tool used to manufacture plastic containers, typically through the injection molding process. Crafted from high-strength materials such as steel or aluminum, the mold consists of one or more cavities that define the final shape and structure of the container. During the injection molding process, molten plastic is injected into the mold, cooled, and solidified to form a finished container with exact dimensions and intended functionality.
The mold is the cornerstone of the plastic container manufacturing process, converting raw plastic material into practical, everyday products. These molds are used for creating a wide variety of plastic items, from food containers to industrial storage solutions, ensuring consistency, quality, and durability in mass production.

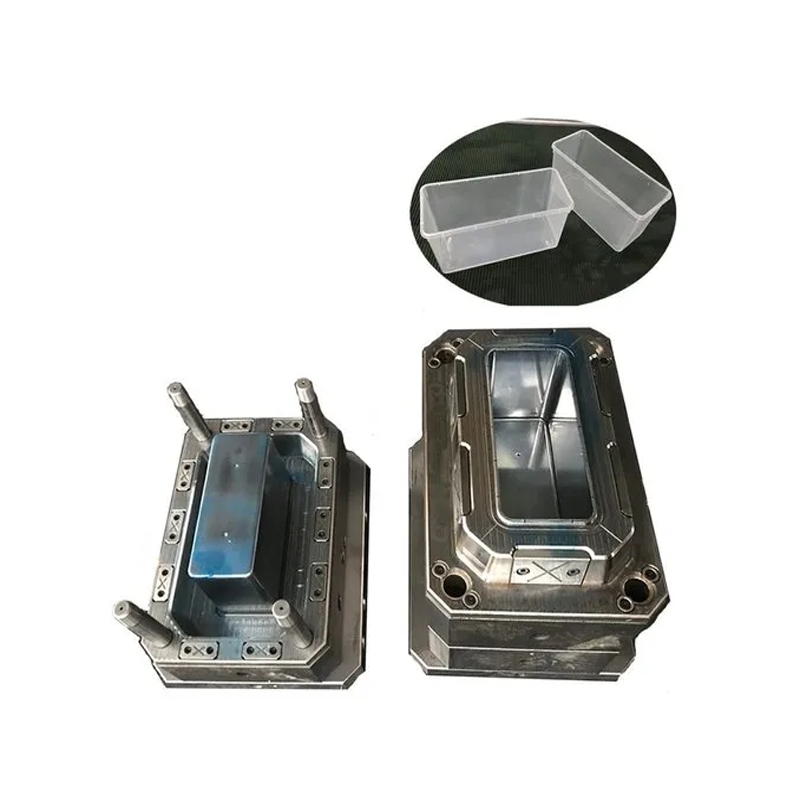
Characteristics of Plastic Container Molds
Several characteristics define the quality and functionality of a plastic container mold. These features stem from the mold’s design, material choice, and manufacturing techniques, all of which are tailored to meet the production requirements for different container types. Key characteristics of plastic container molds include:
– Durability and Strength: Molds are built to withstand the high pressures and temperatures involved in injection molding. Materials like steel and aluminum are chosen for their durability, ensuring that the mold can endure the wear and tear of continuous use. This durability also translates to the longevity of the containers produced, many of which are dishwasher safe for added convenience.
– Versatility and Flexibility: The design of plastic container molds is highly adaptable, allowing for customization based on size, shape, and color. Whether producing containers for food, medical, or industrial applications, plastic molds can be tailored to meet the specific needs of customers. This versatility makes plastic containers suitable for a broad range of industries and applications.
– Efficient Production: One of the most significant advantages of plastic container molds is their efficiency in mass production. The injection molding cycle is relatively quick, typically taking seconds to a few minutes to complete, which allows for high production rates and cost-effective manufacturing.
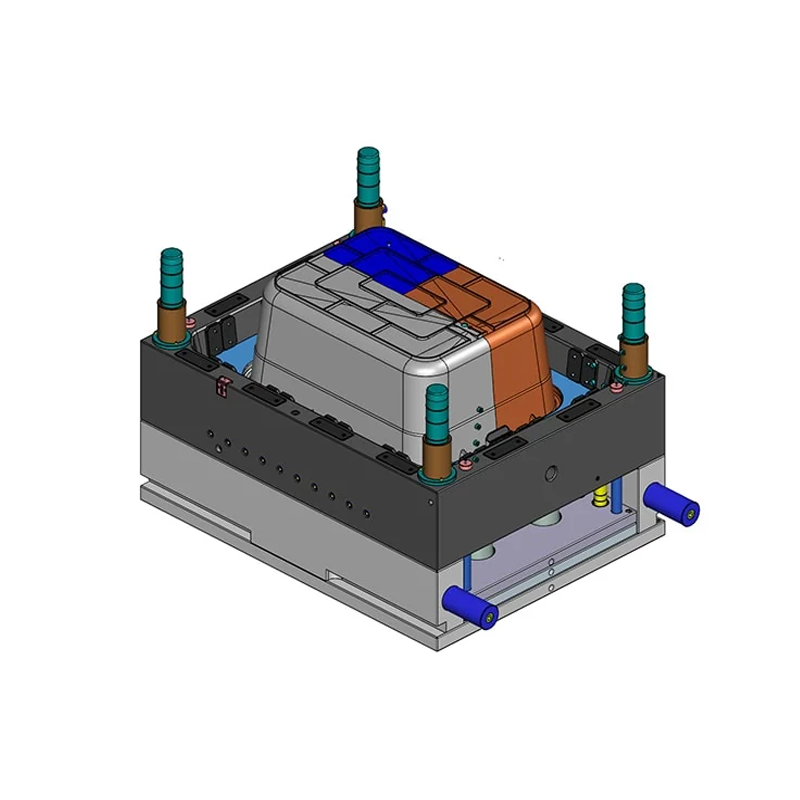
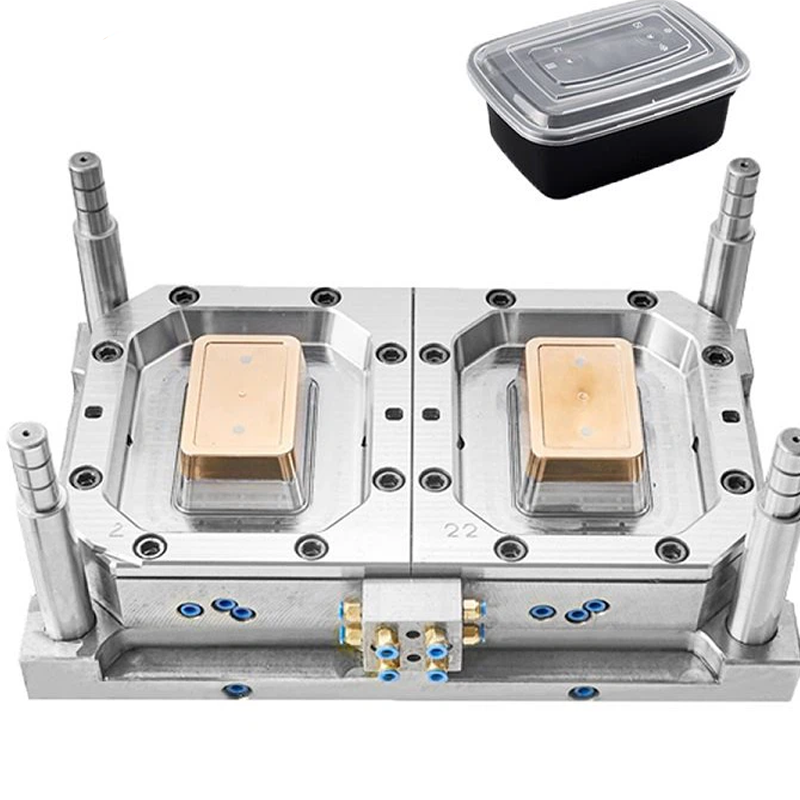
Types of Plastic Container Molds
Plastic container molds can be categorized based on the molding process used, each offering specific advantages depending on the application:
– Injection Molds: These molds are the most commonly used for plastic containers, especially for producing precise and complex shapes such as beverage bottle caps or food packaging. The advantages of injection molds include high production efficiency and consistency across large production runs.
– Blow Molds: Blow molding is used to create hollow containers, such as plastic bottles and tanks, by inflating a heated plastic parison inside a mold. This process can be performed using extrusion blow molding, injection blow molding, or stretch blow molding techniques, all of which are ideal for mass-producing lightweight containers with uniform wall thickness.
– Extrusion Molds: Extrusion molding is used to produce continuous shapes such as pipes, rods, and films. In this process, the plastic is melted and forced through a die to form long, continuous products. This technique is suitable for high-volume production of plastic containers that require uniformity and strength.
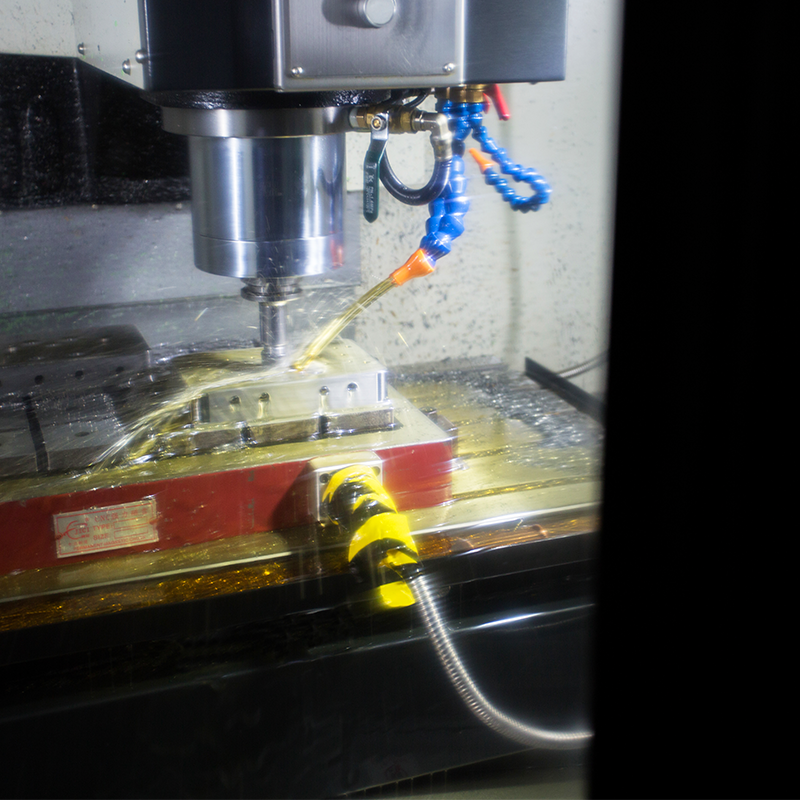
Key Design Considerations for Plastic Container Molds
The effectiveness of a plastic container mold depends on several critical design factors that influence production efficiency, mold longevity, and the quality of the final product:
– Geometry and Complexity: The shape and complexity of the container design directly impact the mold design. For instance, cylindrical containers require smooth, uniform cavities, while containers with sharp edges or intricate features, such as snap-fit lids or recessed handles, may require undercuts and side actions in the mold design.
– Cooling System Design: Uniform cooling is essential to reduce cycle time and ensure consistent product quality. Uneven cooling can lead to warping, internal stresses, or surface imperfections. A well-designed cooling system maximizes heat transfer and ensures the mold’s performance, often incorporating high-conductivity materials like beryllium copper inserts for improved cooling in high-heat zones.
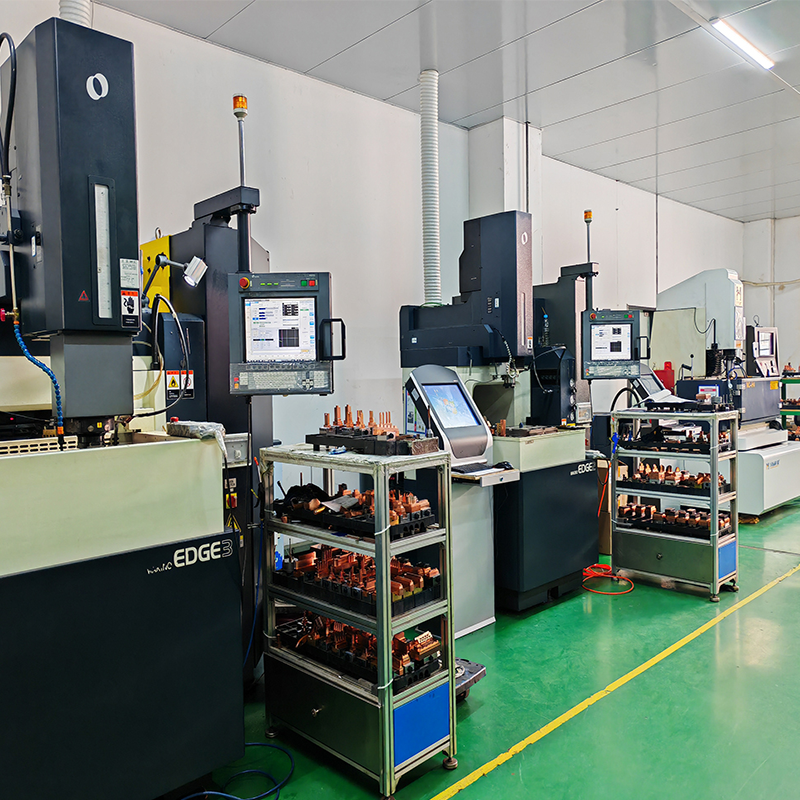

– Ejection Mechanism: The ejection system ensures that the molded container is released from the mold without damage. Ejector pins are strategically placed to push the container out evenly, avoiding visible marks or damage to critical areas. The placement and number of ejector pins are calculated based on the container’s size and tendency to stick to the mold.
– Venting: Proper venting is necessary to prevent air from being trapped during the injection process. Air pockets can lead to defects such as burn marks or incomplete fills, so well-placed vents allow displaced air to escape during injection.
How to Make an Injection Mold for Plastic Containers
Creating an injection mold for plastic containers is a step-by-step process that involves careful planning, material selection, and precision fabrication:
- Select Mold Material: Choosing the right material for the mold is crucial for its durability and performance. Steel, particularly P20 and H13, is commonly used for its toughness and resistance to high temperatures, while aluminum is preferred for prototype molds due to its ease of machining.
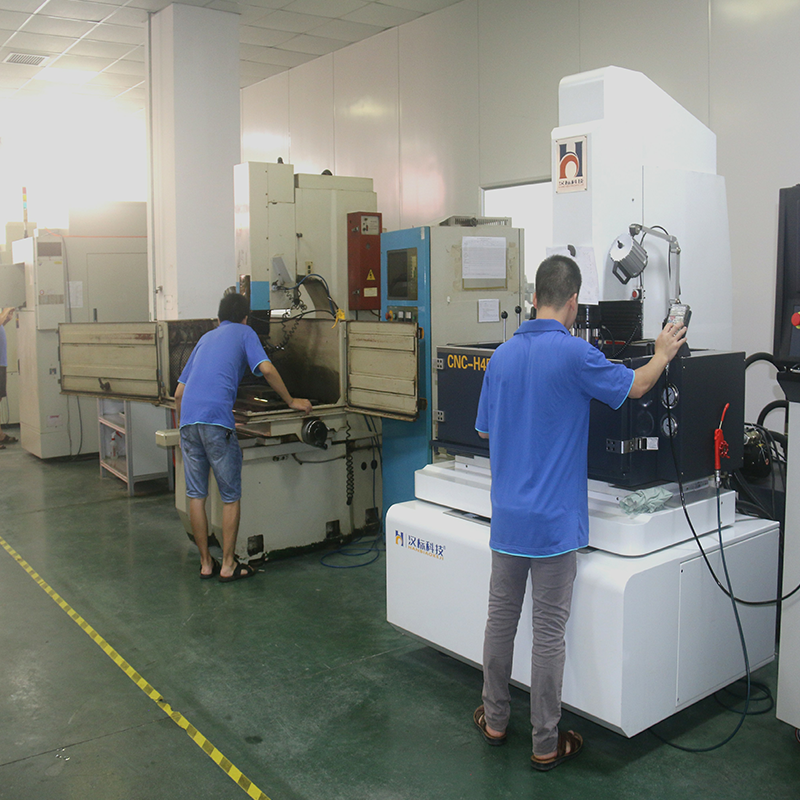
- Fabricate the Mold: Using a CNC milling machine, the mold base, cavities, and cores are precisely cut. Electrical discharge machining (EDM) is used to create intricate details. The cavity and core halves are aligned using guide pins to ensure accuracy.
- Finish and Treat the Surface: The mold cavities are smoothed to achieve the desired finish, and surface treatments such as chrome plating may be applied to enhance wear resistance and provide aesthetic appeal.
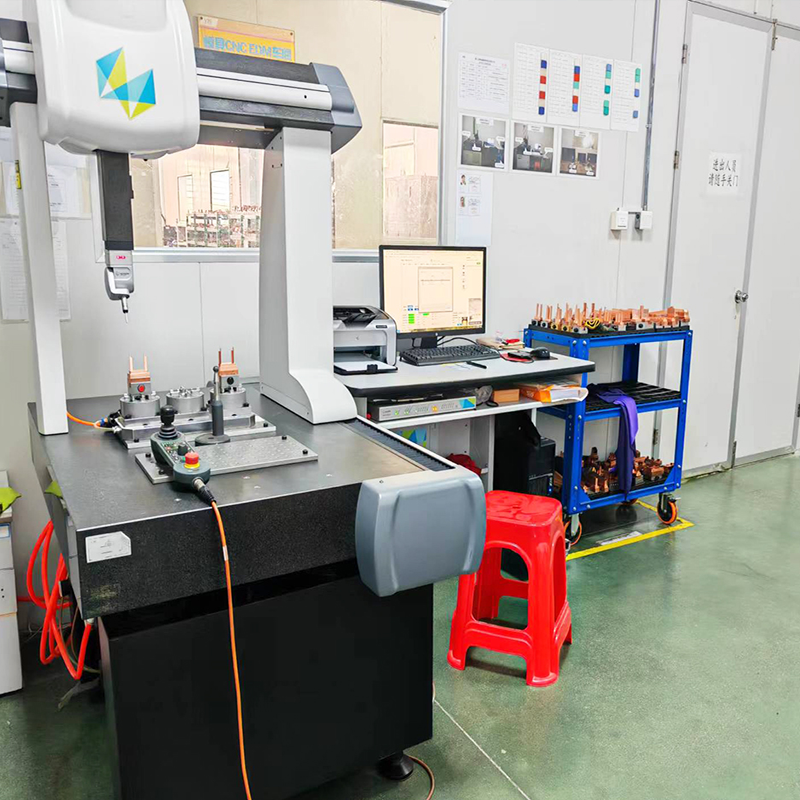
- Test and Refine the Mold: After fabrication, the mold is tested by injecting plastic and producing sample containers. Any defects, such as warping or incomplete filling, are addressed by modifying the mold—adjusting cooling channels, resizing vents, or repositioning ejector pins as necessary.

Applications of Plastic Container Molds
Plastic container molds are utilized in various industries to produce functional containers for a wide range of applications:
– Food and Beverage Packaging: Molds produce food-grade containers such as beverage bottles, yogurt cups, and food storage boxes. These molds must comply with hygiene standards and produce lightweight, durable, and recyclable products.
– Industrial and Logistics Storage: Large plastic containers, such as pallets and bins, are manufactured using molds that require strength and load-bearing capabilities. These containers are used for chemical transport, warehousing, and logistics applications.
– Household Consumer Goods: Molds are also used for manufacturing common household items such as storage bins, trash cans, and kitchen tools.
– Pharmaceutical and Healthcare: Medical-grade containers, including medicine bottles and reagent storage boxes, are produced with high precision to meet industry standards for safety and sterility.

Future Trends in Plastic Container Mold Technology
As industries increasingly focus on sustainability and customization, plastic container mold technology continues to evolve. Future trends include:
– Sustainable Materials: The adoption of biodegradable plastics and recycled materials is driving the development of molds that can handle these materials without compromising performance or product quality.
– Smart Molds: Integrating smart sensors into molds will allow for real-time monitoring of temperature, pressure, and cycle time, enhancing production efficiency and reducing downtime.
– Additive Manufacturing: 3D printing technology is enabling the rapid prototyping of complex mold designs, offering faster turnaround times and more flexibility in production.

Conclusion
Plastic container molds are crucial in the manufacturing of high-quality containers across diverse industries. The design, material selection, and manufacturing techniques involved in producing these molds determine the quality, efficiency, and sustainability of the containers they produce. At LSRmold, we are at the forefront of this industry, offering customized plastic container mold solutions to meet your specific needs. Our experienced team is committed to delivering cost-effective and high-performance molds tailored to your requirements. If you’re ready to start your next container mold project, contact LSRmold today for a competitive quote and expert guidance!

